
Adjusting entries are prepared as an application of the accrual concept of accounting. At the end of the accounting period, some expenses may have been incurred but not yet recorded in the journals. The last step in the accounting cycle is preparing financial statements—they’ll tell you where your money is and how it got there. It’s probably the biggest reason we go through all the trouble of the first five accounting cycle steps. Once you identify your business’s financial accounting transactions, it’s important to create a record of them.
Accounting for Tech Companies: Overview and Best Practices
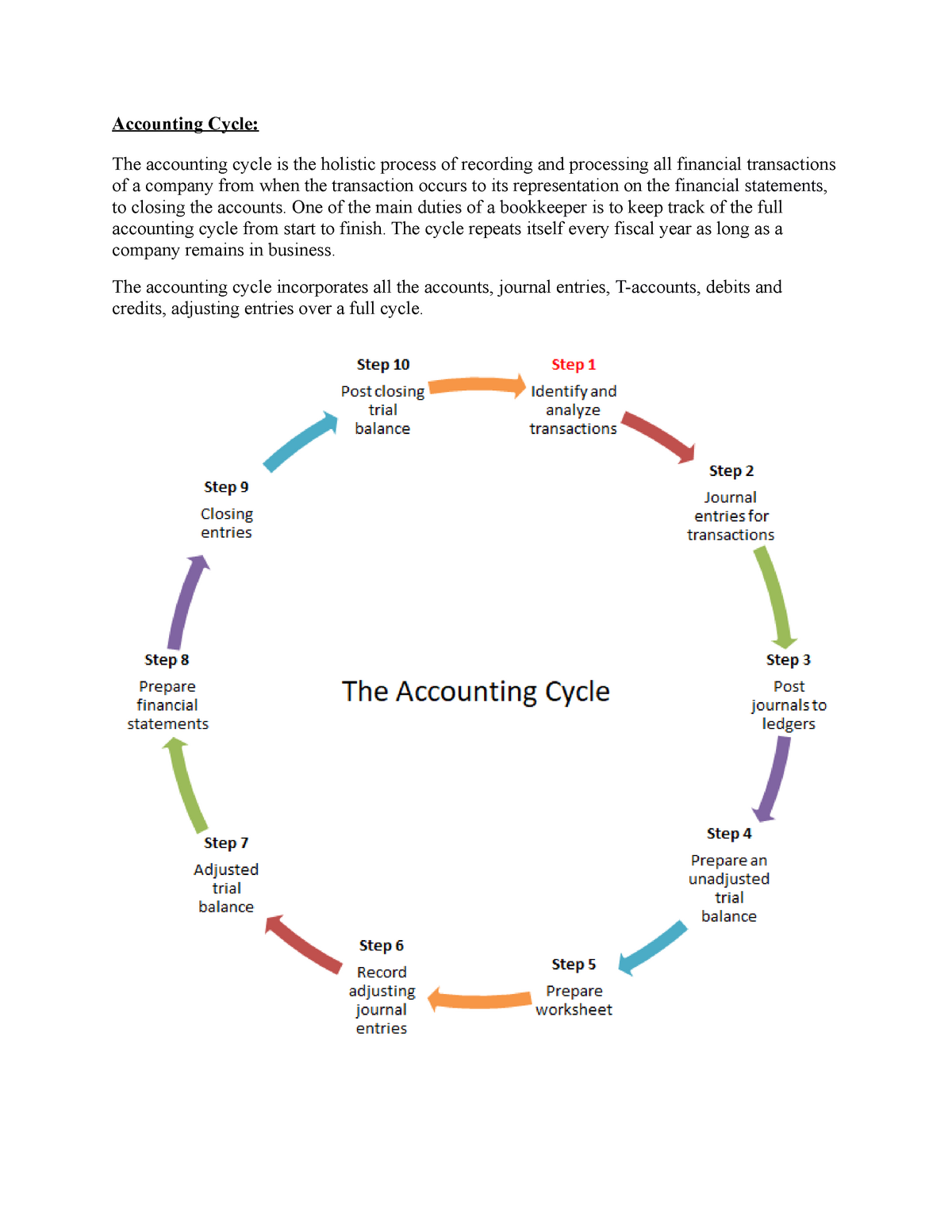
Its format is similar to that of an unadjusted and adjusted trial balance. However, it lists only permanent accounts because all temporary accounts get closed in step 8 above. The post-closing trial balance serves as the base or opening trial balance for the next period’s accounting cycle. After the adjusting entries have been passed and posted to respective ledger accounts, the unadjusted trial balance needs to be corrected to show the impact of these adjustments. For this purpose, an amended trial balance, known as an adjusted trial balance, is prepared.
Step 6: Prepare financial statements
The first step in the accounting cycle is identifying transactions. Companies will have many transactions throughout the accounting cycle. Every individual company will usually need to modify the eight-step accounting cycle in certain ways in order to fit with their company’s business model and accounting procedures. Modifications for accrual accounting versus cash accounting are often one major concern. The accounting cycle is used comprehensively through one full reporting period.
Steps in accounting cycle
They are prepared at the beginning of the new accounting period to facilitate a smoother and more consistent recording process, especially if the company uses a cash-basis accounting system. First, an income statement can be prepared using information from the revenue and expense account sections of the trial balance. This new trial balance is called an adjusted trial balance, and one of its purposes is to prove that all of your ledger’s credits and debits balance after all adjustments. Once you’ve posted all of your adjusting entries, it’s time to create another trial balance, this time taking into account all of the adjusting entries you’ve made. Journal entries are usually posted to the ledger as soon as business transactions occur to ensure that the company’s books are always up to date. The next step in the accounting cycle is to post the transactions to the general ledger.
- Next, you’ll break down (or analyze) the purpose of each transaction.
- He worked with TIME, Observer, HuffPost, Adobe, Webflow, Envato, InVision, and BigCommerce.
- However, you also need to capture expenses, which you can do by integrating your accounting software with your company’s bank account so that every payment will be charged automatically.
- However, businesses with internal accounting cycles also follow the external accounting cycle of the fiscal year.
Your accounting type and method determine when you identify expenses and income. For accrual accounting, you’ll identify financial transactions when they are incurred. Meanwhile, cash accounting involves looking for transactions whenever cash changes hands. A business starts its does prepaid rent affect net income by identifying and gathering details about the transactions made during the accounting period. When identifying a transaction, you’ll need to determine its impact. Transactions include expenses, asset acquisition, borrowing, debt payments, debts acquired and sales revenues.
The main purpose of drafting an unadjusted trial balance is to check the mathematical accuracy of debit and credit entries recorded under previous steps. From identifying transactions to preparing financial statements, the 8 steps in the accounting cycle ensure accurate record-keeping. The last step in the accounting cycle is to make closing entries by finalizing expenses, revenues and temporary accounts at the end of the accounting period. This involves closing out temporary accounts, such as expenses and revenue and transferring the net income to permanent accounts like retained earnings. The balance sheet and income statement depict business events over the last accounting cycle.
Double-entry accounting suggests recording every transaction as a credit or debit in separate journals to maintain a proper balance sheet, cash flow statement and income statement. Meanwhile, single-entry accounting is more like managing a checkbook. It doesn’t require multiple entries but instead gives a balance report.
Now it’s time to record the above transaction in the general Journal. To gain a better understanding of this, consider an error in the general ledger. This entry needs to reference where the error exists so that anyone reviewing it can verify it for accuracy. Each one of them relates to an accounting transaction that has taken place. We’re going to go over all of the steps and provide examples of what each step would look like.
However, the most common type of accounting period is the annual period. The accounting cycle is an eight-step process that accountants and business owners use to manage the company’s books throughout a specific accounting period, such as the fiscal year. The accounting cycle is critical because it helps to ensure accurate bookkeeping. Skipping steps in this eight-step process will likely lead to an accumulation of errors.
These journal entries are known as adjusting entries, which ensure that the entity has recognized its revenues and expenses in accordance with the accrual concept of accounting. The accounting cycle is the backbone of financial management and reporting. From recording transactions to preparing financial statements, each stage of the accounting cycle plays an important role in making sure a business’s financial information is accurate and up to date. Here’s an in-depth look at the accounting cycle, including the eight primary steps involved and how accounting software can help. The accounting process consists of activities involved in preparing financial statements and includes identifying, recording, and summarizing a business’s financial transactions. The accounting cycle is the series of steps required to complete the accounting process.